Online Titanium Parts 3D Printing Service
Experience precision and innovation with our titanium parts 3D printing service. Utilizing Powder Bed Fusion, Binder Jetting, Sheet Lamination, and Directed Energy Deposition, we deliver high-quality, customized titanium components for diverse applications.
- Powder Bed Fusion 3D Printing
- Binder Jetting 3D Printing
- Sheet Lamination 3D Printing
- Directed Energy Deposition 3D Printing

Send us your designs and specifications for a free quotation
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
Titanium 3D Printing Technologies
Titanium 3D printing leverages advanced technologies like DMLS, SLM, EBM, Binder Jetting, LMD, EBAM, WAAM, UAM, and LOM. These methods enable high-precision, cost-effective production of titanium parts, catering to aerospace, medical, and industrial applications with exceptional mechanical properties and scalability.
Titanium 3D Printing Materials
Post Process for 3D Printed Titanium Parts
Optimize the performance and quality of titanium parts with advanced post-processing methods, including CNC machining, EDM, heat treatment, HIP, thermal barrier coatings, and surface treatments, ensuring enhanced durability, precision, and application-specific functionality.
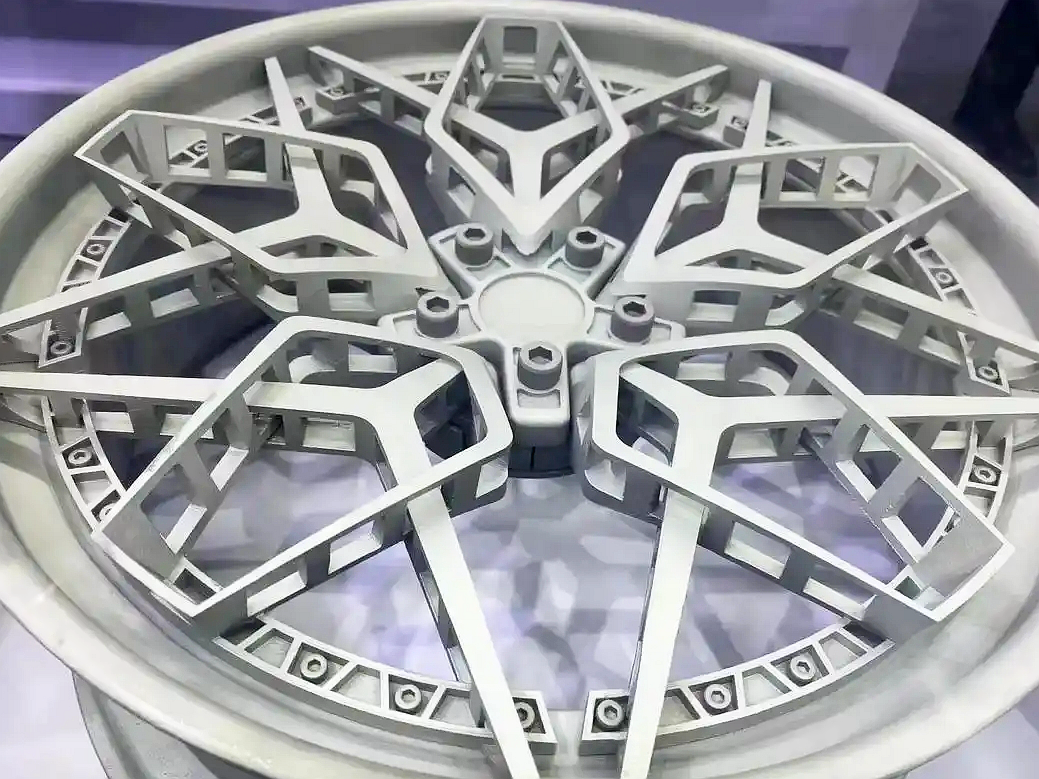
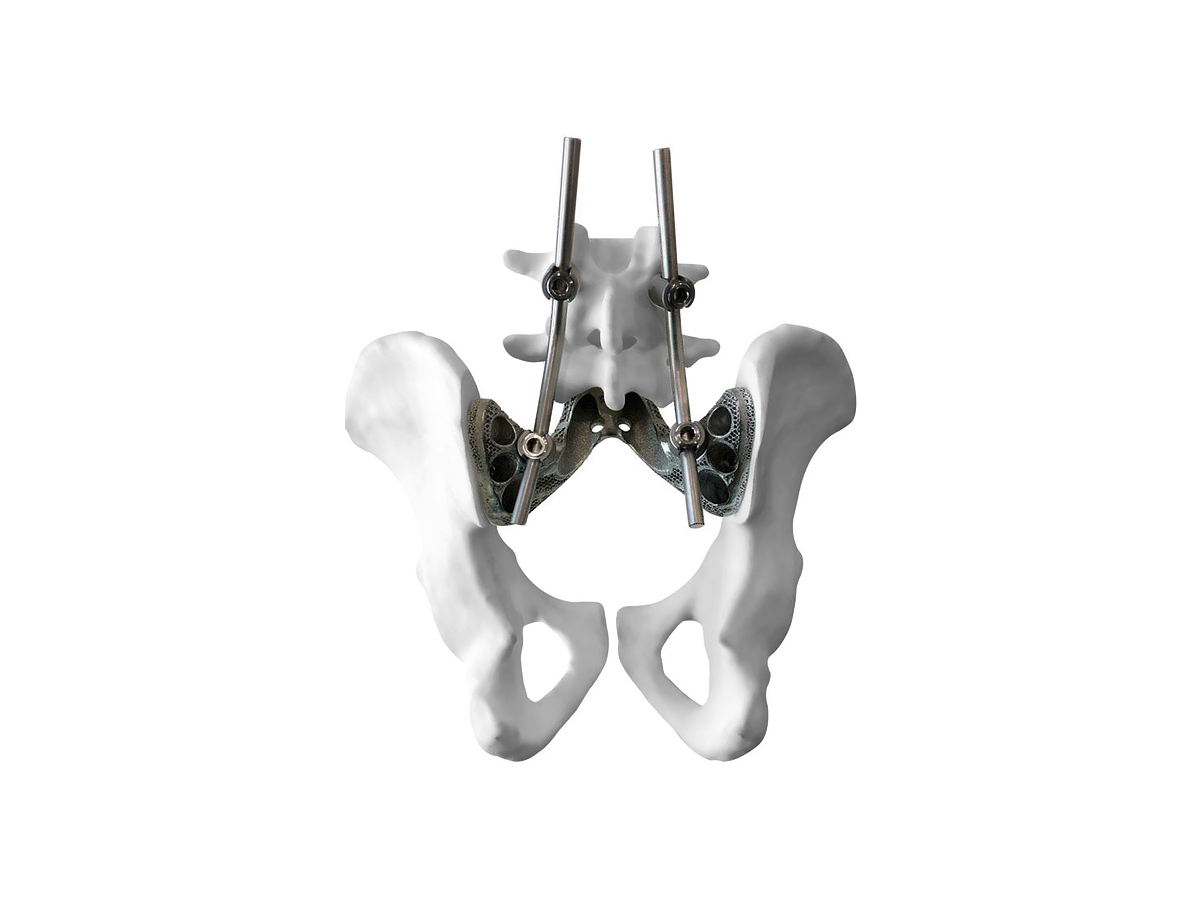
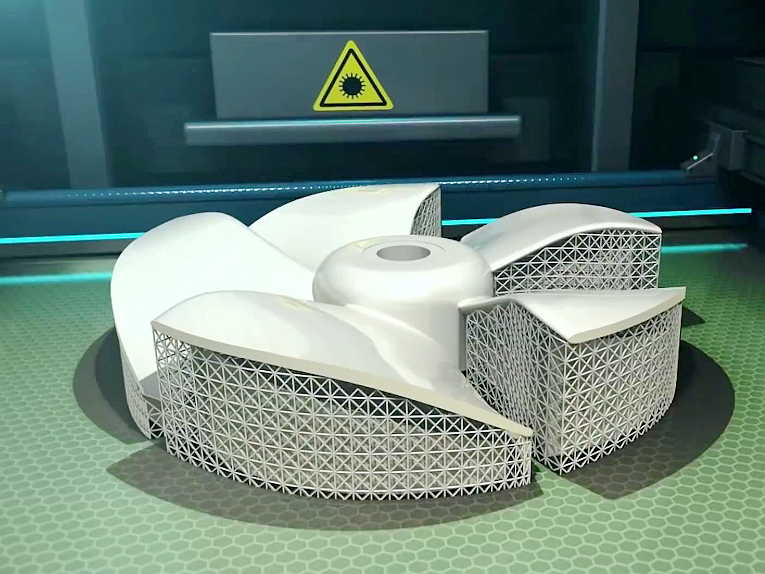
Applications of Titanium 3D Printed Parts
Titanium 3D printed parts are celebrated for their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making them indispensable across a variety of sectors. These parts are particularly useful in industries requiring lightweight but strong materials, as well as high precision and complex geometries.
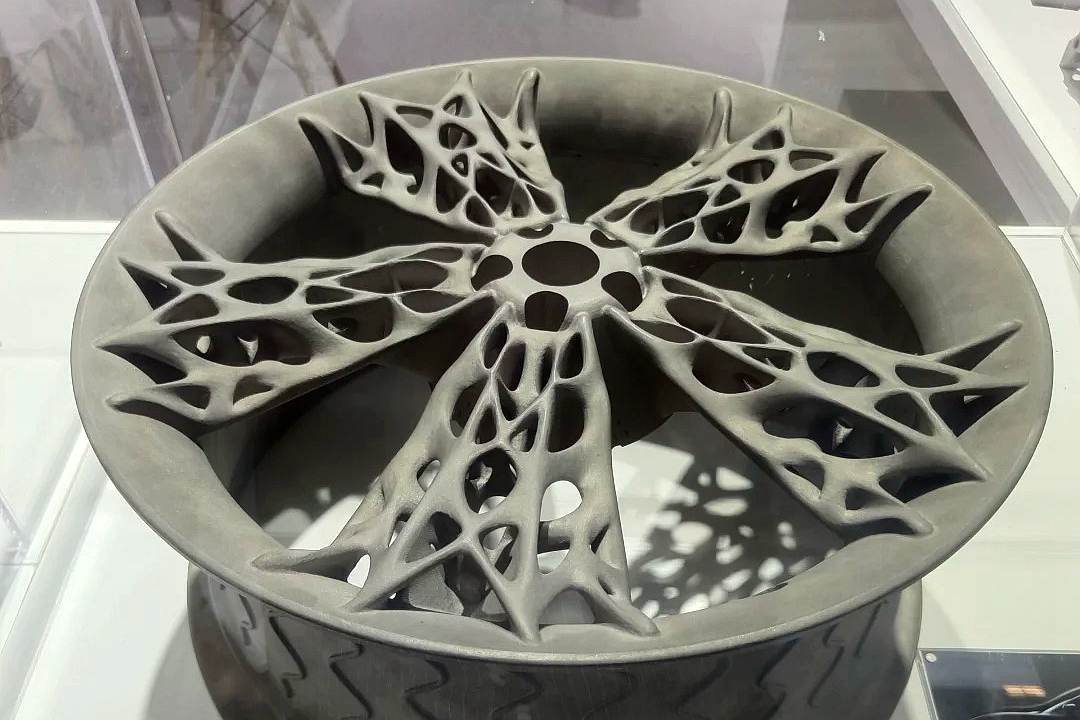
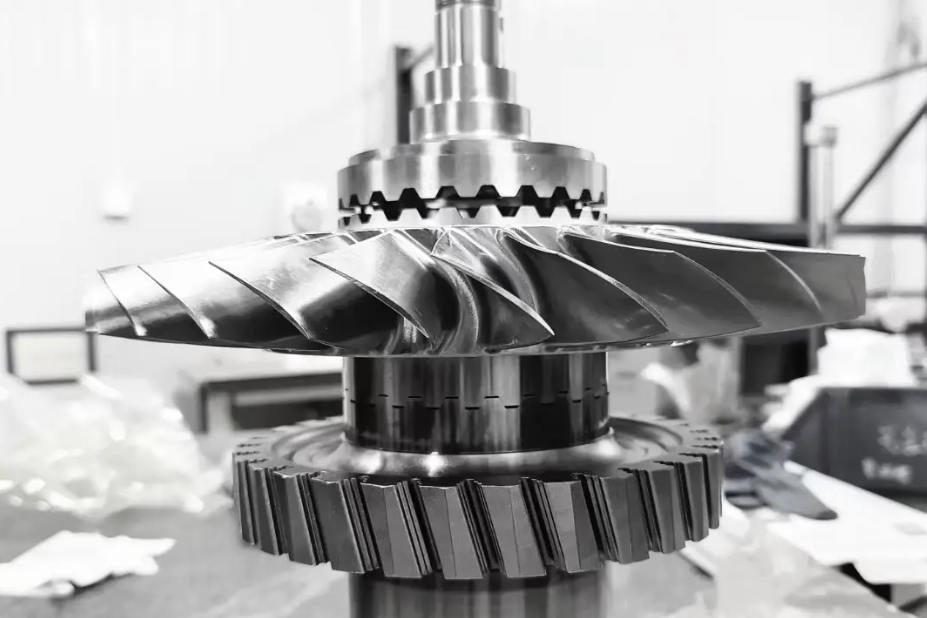
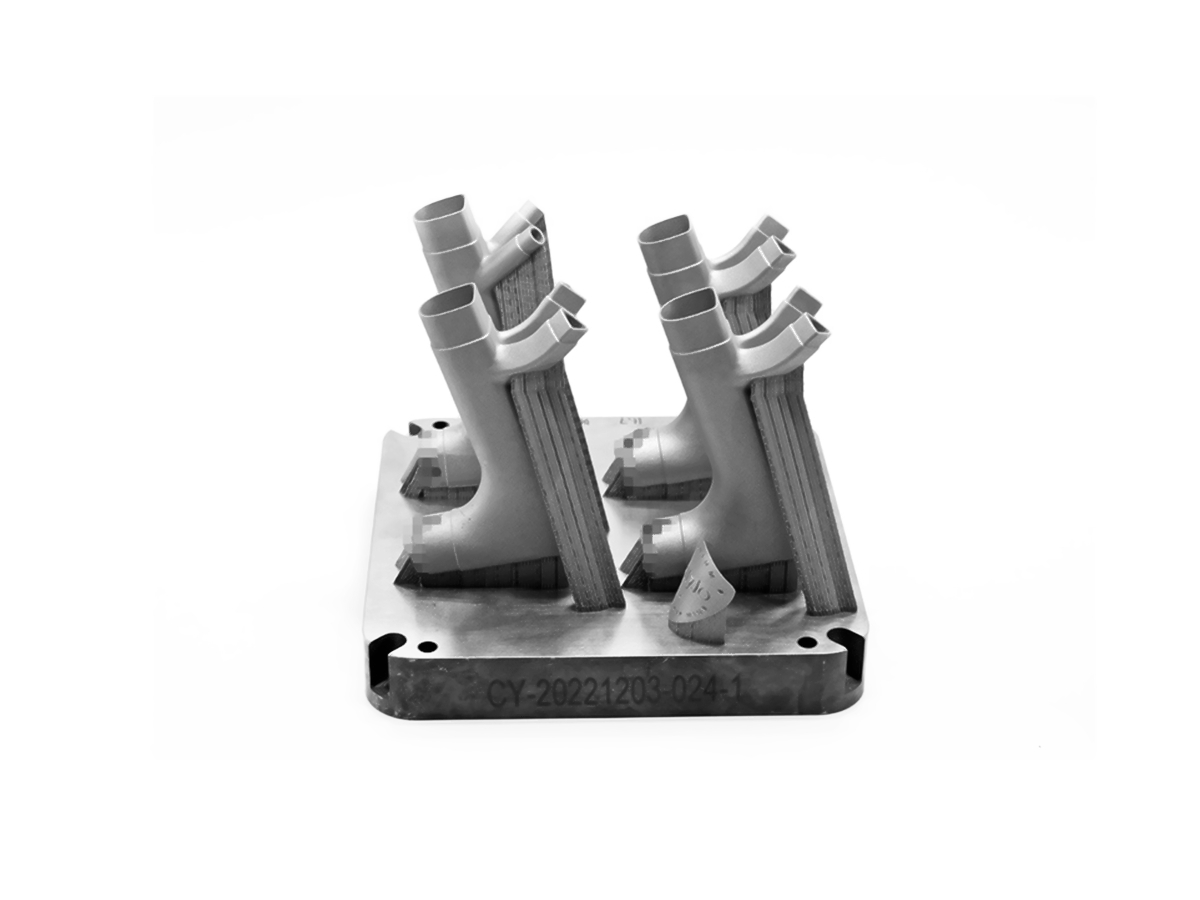
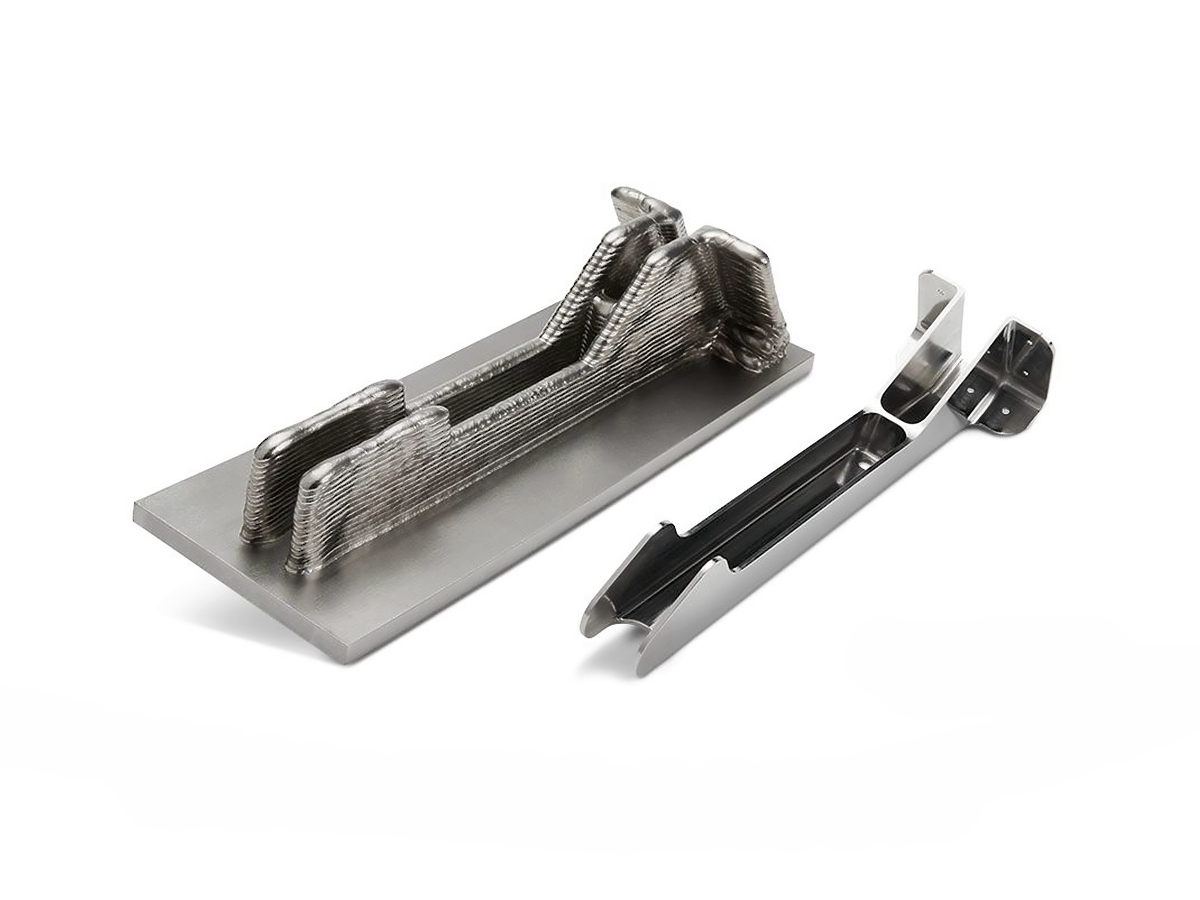
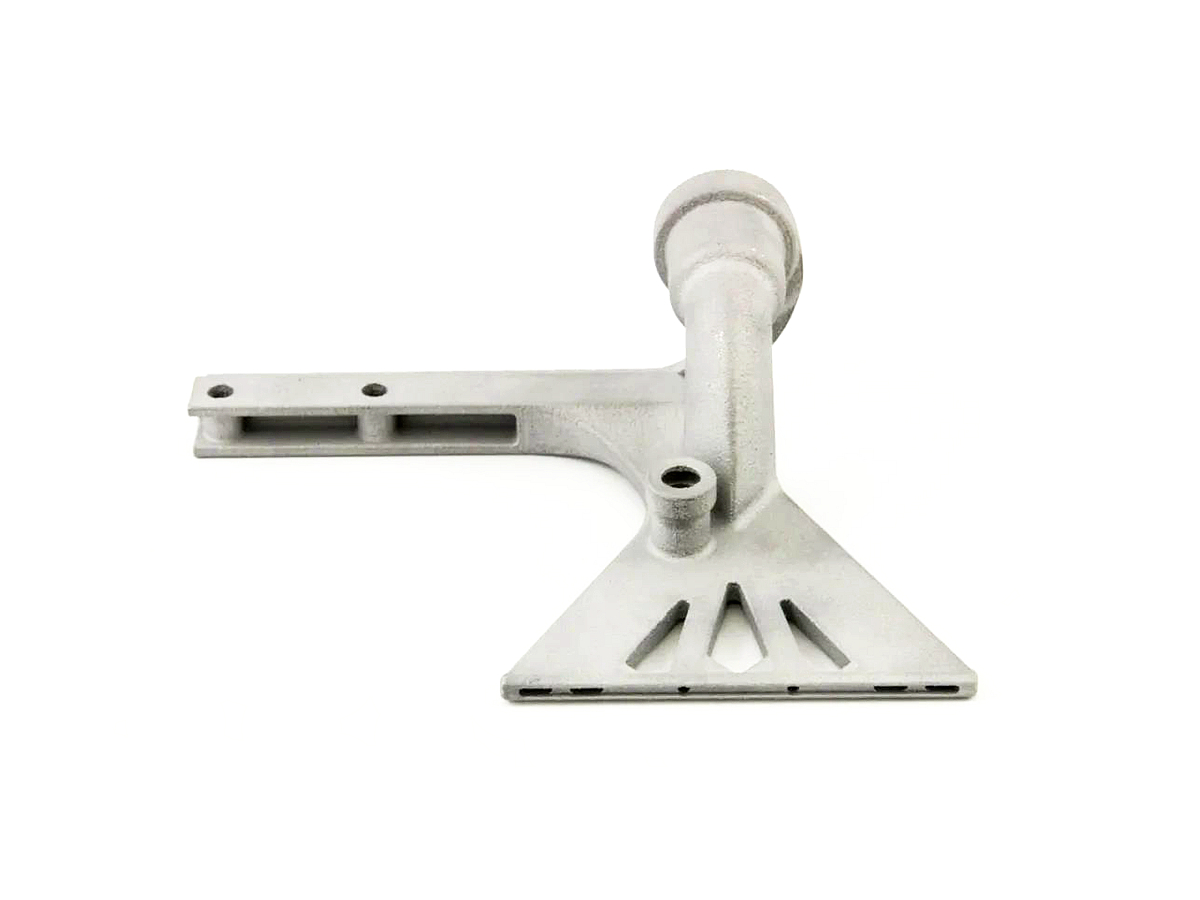
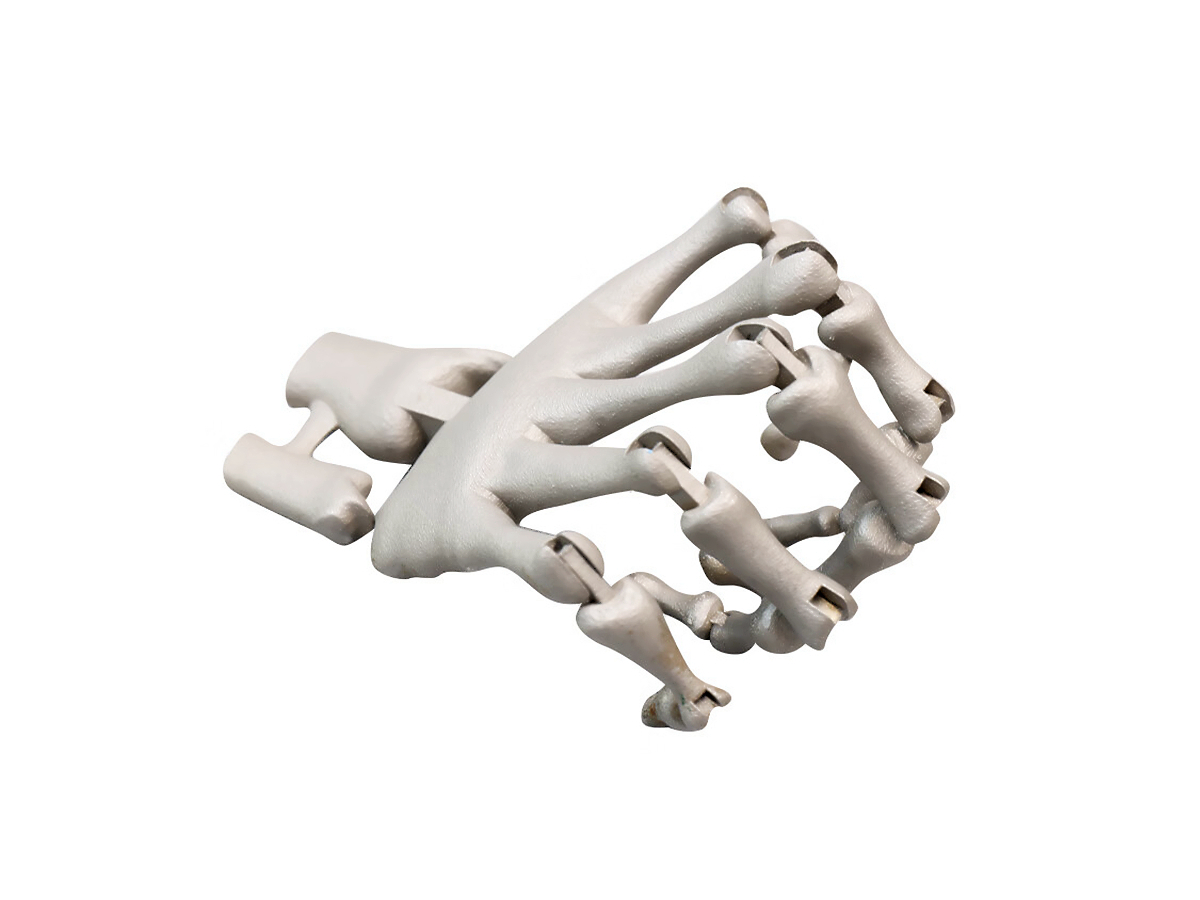
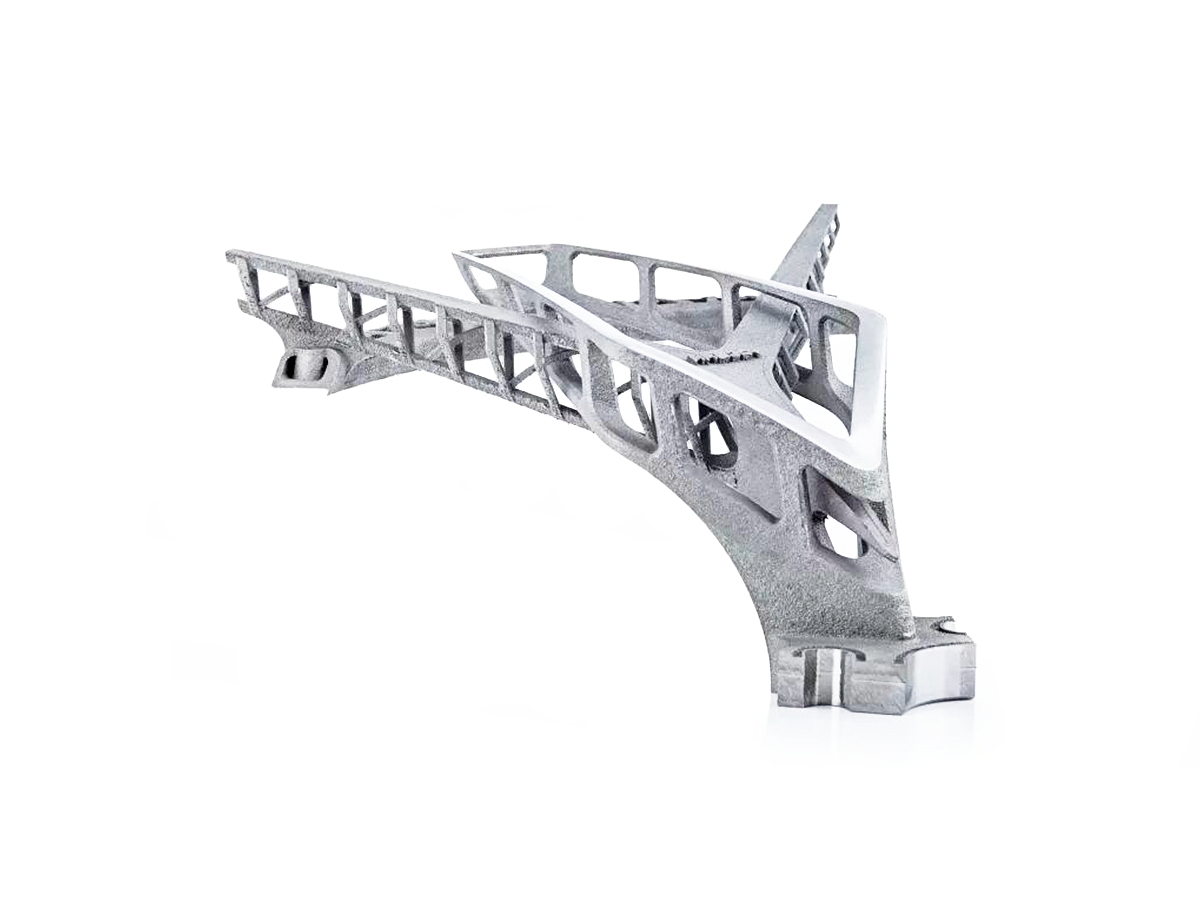
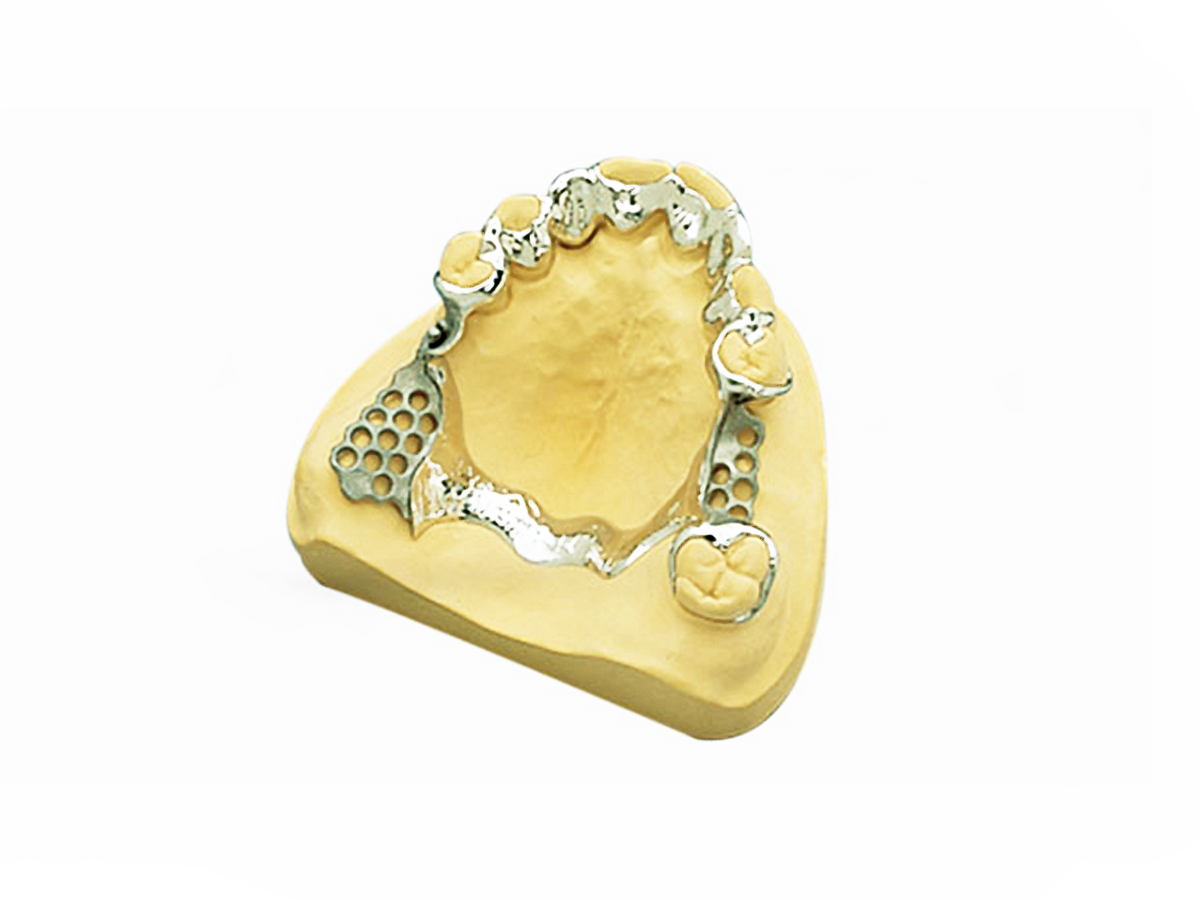
Titanium 3D Printed Parts Case Study
Titanium 3D Printed Parts Case Study explores how advanced titanium 3D printing delivers high-strength, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant solutions for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. From custom prosthetics and dental implants to durable automotive components and aerospace brackets, this study highlights precision manufacturing, rapid prototyping, and superior performance in demanding applications.
Let's Start A New Project Today
Titanium 3D Printed Parts Design Considerations
When designing titanium 3D printed parts, consider wall thickness, tolerance, and hole design for structural integrity. Utilize supports for critical overhangs and optimize part orientation for enhanced print quality. Implement thermal management strategies to avoid deformation, efficiently integrate lattice structures for weight reduction, and address stress concentrations with smooth transitions. Post-print heat treatments are essential for enhancing mechanical properties and relieving stress.
Titanium Alloy 3D Printed Parts Manufacturing Considerations
Manufacturing considerations for titanium alloy 3D printed parts are essential to harness the material's high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Key factors include controlling the printing environment to avoid contamination, managing thermal stresses, and ensuring optimal mechanical properties through precise post-processing techniques.